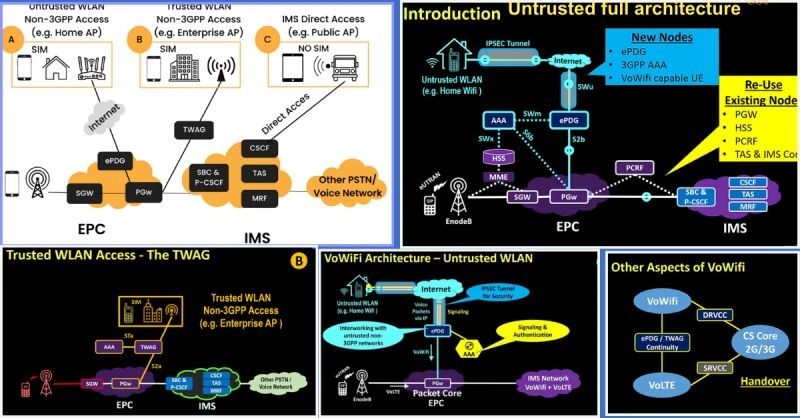
𝗩𝗼𝗶𝗰𝗲 𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿 𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶 (𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶)
𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶 (𝗩𝗼𝗶𝗰𝗲 𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿 𝗪𝗶-𝗙𝗶) is a technology that allows users to make voice calls over a Wi-Fi instead of a cellular network.
Its Architecture is composed of:
𝟭. 𝗪𝗶-𝗙𝗶 𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸:
It can be any Wi-Fi access point, such as home routers, public Wi-Fi, or enterprise networks.
Does not process mobile signaling but provides the IP transport for voice data packets.
It could be:
🚀 𝗨𝗻𝘁𝗿𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸: When the Wi-Fi network is not managed by the mobile operator (e.g., public Wi-Fi hotspots or home networks).
🚀 𝗧𝗿𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸: one that is managed or approved by the operator (e.g., operator-controlled Wi-Fi hotspots or enterprise network.)
🚀 𝗗𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗰𝘁 𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶 𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀: UE connects directly to the IMS core over Wi-Fi 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵𝗼𝘂𝘁 𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚.
𝟮. 𝗘𝘃𝗼𝗹𝘃𝗲𝗱 𝗣𝗮𝗰𝗸𝗲𝘁 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗚𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘄𝗮𝘆 (𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚) or 𝗧𝗿𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗪𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗹𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗚𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘄𝗮𝘆 (𝗧𝗪𝗔𝗚):
𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚 acts as a secure interface b/n the untrusted Wi-Fi network & the operator’s core network.
🚀 Establishes an 𝗜𝗣𝘀𝗲𝗰 𝘁𝘂𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹 with the user’s device for secure communication over Wi-Fi.
🚀 Ensures authentication using credentials stored in the SIM (e.g., 𝗜𝗠𝗦𝗜) in collaboration with HSS and the AAA Server.
𝗧𝗪𝗔𝗚 is used when the Wi-Fi network is trusted by the mobile operator.
🚀 It functions as a bridge b/n the Wi-Fi network and the operator’s core network.
🚀 It does not use IPsec tunnels like the ePDG. Instead, it relies on the inherent security of the managed Wi-Fi network.
🚀 It supports direct access to the Packet Gateway (P-GW) without requiring an 𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚.
𝟯. 𝗘𝘅𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗖𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸 𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 with 𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶 adaptation to operate with the new interfaces, protocols & authentication capability. This includes (𝗜𝗠𝗦, 𝗛𝗦𝗦, 𝗔𝗔𝗔, 𝗣-𝗚𝗪, 𝗠𝗚𝗪, 𝗣𝗖𝗥𝗙.)
𝟰. 𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗳𝗶 𝗰𝗮𝗽𝗮𝗯𝗹𝗲 𝘂𝘀𝗲𝗿 𝗱𝗲𝘃𝗶𝗰𝗲 (𝗨𝗘):
The user’s smartphone or tablet, equipped with VoWiFi functionality ( 𝗦𝗜𝗣 𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿 𝗮𝗻 𝗜𝗣𝘀𝗲𝗰 𝘁𝘂𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹) to the 𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚.
𝗖𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗙𝗹𝗼𝘄 𝗶𝗻 𝗩𝗼𝗪𝗶𝗙𝗶
𝟭. 𝗗𝗲𝘃𝗶𝗰𝗲 𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗵𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻:
The device connects to the 𝗲𝗣𝗗𝗚 over Wi-Fi(permitted by AAA), creating a secure IPsec tunnel or directly to the 𝗧𝗪𝗔𝗚 in the case of 𝘁𝗿𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗱 WiFi.
Use 𝗛𝗦𝗦 to authenticate the SIM credentials.
𝟮. 𝗜𝗠𝗦 𝗥𝗲𝗴𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻:
Once authenticated, the 𝗨𝗘 registers with the IMS core using 𝗦𝗜𝗣.
𝟯. 𝗖𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗘𝘀𝘁𝗮𝗯𝗹𝗶𝘀𝗵𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁:
When a call is made, 𝗦𝗜𝗣 sets up the session b/n the calling & receiving parties.
Voice data flow via Wi-Fi network to the 𝗜𝗠𝗦 𝗰𝗼𝗿𝗲 & the recipient.
𝟰. 𝗛𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿:
If the user moves out of Wi-Fi coverage, the call seamlessly transitions to 𝗩𝗼𝗟𝗧𝗘 via the 𝗜𝗠𝗦 core, maintaining continuity or 𝗦𝗥𝗩𝗖𝗖 may be used to handover to legacy 𝗖𝗦.