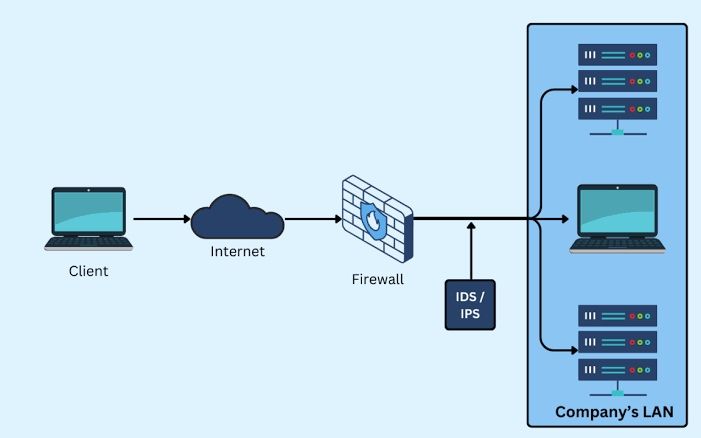
Simply put, an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) functions like a security guard that monitors all activity within a network. If it detects any threats, it immediately stops the attack before any damage occurs. This differs from traditional security systems, such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), which only detect threats and send alerts without taking direct action.
# How Does IPS Work?
An IPS is installed in the direct path between the source and destination, meaning it analyzes traffic as it flows between devices in real-time. If the IPS identifies threats, such as attacks on systems or applications, it takes prompt measures to mitigate the threat. This may involve dropping or redirecting malicious data or even disconnecting malicious entities to prevent them from spreading.
# Types of IPS:
1. **NIPS (Network Intrusion Prevention System)**:
NIPS are strategically placed within the network, such as at the perimeter or in major data centers. Their role is to monitor traffic and identify attacks before they can propagate between devices.
2. **HIPS (Host Intrusion Prevention System)**:
HIPS is installed directly on individual devices or servers. It focuses on monitoring traffic specific to that host, preventing attacks before they can reach the device’s content.
3. **WIPS (Wireless Intrusion Prevention System)**:
WIPS specializes in monitoring wireless networks (Wi-Fi). It protects against unauthorized devices and attempts to detect any threats over the wireless medium.
4. NBA (Network Behavior Analysis)*
This type analyzes traffic to detect abnormal or unusual patterns indicative of attacks, such as DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attacks.
# How Does IPS Detect Attacks?
IPS technology employs several methods for attack detection:
*Signature-based Detection*
This method relies on databases of known attack signatures. If the system detects activity that matches a specific entry in these databases, it takes immediate action.
*Anomaly-based Detection*
This method compares current traffic data against recorded normal behavior. If it identifies any significant deviations, it initiates a scan to enforce protection.
A key feature of IPS is the “Virtual Patch.” This allows it to address vulnerabilities in the system without requiring direct platform updates. The IPS enforces a temporary security policy to protect the network from attacks targeting specific vulnerabilities.
# Types of Attacks Stopped by IPS:
An IPS can thwart various types of attacks, including:
*DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service)*
Attacks aimed at overwhelming the network with excessive traffic, resulting in service disruption.
*ARP Spoofing*
An attack that seeks to manipulate the MAC address of a specific device within the network.
*Buffer Overflow*
Exploiting vulnerabilities in the system to write malicious data into memory.
*SYN Flood*
An attack designed to inundate the system with a large volume of connection requests.
By utilizing various detection methods and proactive measures, an IPS plays a crucial role in safeguarding networks from numerous threats.