📘 Why Learn About Ports?
When you work with computers, networking, CCTV or IT infrastructure, half of your troubleshooting is simply “which port should this cable go into?”. If you mis-plug or force a wrong connector, you can break hardware or waste hours.
This guide walks you through the most important ports you’ll see in real life — PC, laptop, switch, router, NVR, server — with simple explanations and practical tips.
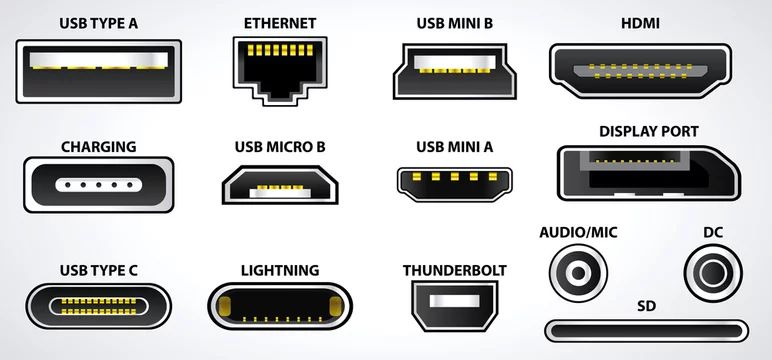
1️⃣ USB Ports (1.0 / 2.0 / 3.x / Type-C)
Use for: keyboard, mouse, pen drive, external HDD/SSD, webcam, printers, phone charging, etc.
Common USB Types
- USB-A (2.0, 3.0, 3.1) – The classic rectangular port.
- USB 2.0 → usually black/white inside. Slower (up to 480 Mbps).
- USB 3.x → usually blue or teal. Faster (5–10 Gbps).
- USB-C – Small oval, reversible (no “up or down”). Supports data, video (DisplayPort/HDMI alt mode), and charging.
- Micro-USB / Mini-USB – Older phones, cameras, some routers, barcode scanners.
Tips
- For external SSD or fast backup, always use a USB 3.x port.
- Some USB ports on laptops are marked with a lightning or battery icon → more power for charging.
- Front panel USB on desktops may be weaker; use back panel for stability.
2️⃣ Network & Telecom Ports
Ethernet (RJ-45)
Use for: wired LAN, connecting PCs, switches, routers, IP phones, IP cameras, access points.
- Looks like a “big telephone plug” with 8 metal contacts.
- Sometimes labeled LAN, WAN, PoE, or numbered (1–24).
- Link/Activity LEDs show connection and traffic.
Telephone (RJ-11)
- Smaller than RJ-45, usually with 2 or 4 contacts.
- Used for analog phones and some DSL modems.
- RJ-11 will physically “fit” in RJ-45 but never do this on a switch port.
Console / Management Ports
- Found on routers, switches, firewalls.
- Can be RJ-45 (console), USB-Mini, USB-C or even old serial DB-9.
- Used for CLI access (initial setup, recovery), not for normal network traffic.
3️⃣ Video / Display Ports
Use for: connecting to monitors, TVs, projectors, KVMs.
- VGA – 15-pin blue connector (analog, older). Ok for basic display, not sharp for high resolution.
- DVI – White connector, digital (better than VGA, older than HDMI).
- HDMI – Most common today; carries digital video + audio; used in PCs, TVs, NVRs, DVRs.
- DisplayPort (DP) – PC/monitor focused; better for high refresh rate gaming/dual monitors.
- Mini DisplayPort / USB-C with DP Alt Mode – Found on laptops; often used with adapters.
- Thunderbolt – Looks like USB-C but supports very high-speed data + video + daisy chaining.
4️⃣ Audio Ports
These are usually 3.5mm round jacks on PCs, laptops, speakers and mixers.
- Headphone / Line-out – Usually green. Sends audio to headphones or speakers.
- Mic-in – Usually pink. For microphones.
- Line-in – Often blue. For input from another audio device (mixer, instrument).
- TRRS combo jack – Single 3.5mm on many laptops (headset + mic in one port).
- Optical (TOSLINK) – Square shaped, red light inside; used for digital audio to sound systems.
5️⃣ Storage & Internal Ports
SATA
- Small L-shaped connector inside desktops/servers for HDDs and SSDs.
- Usually two separate connectors: data (thin) + power (wider).
M.2 / NVMe
- Looks like a small gum-stick SSD mounted flat on the motherboard.
- Slot is called M.2; drive may use NVMe (very fast) or SATA protocol.
Other / Older
- IDE / PATA – Wide ribbon cable on very old PCs.
- SAS – Enterprise servers/storage arrays.
- eSATA – External SATA (now rare, replaced by USB 3.x).
6️⃣ CCTV & Security Ports
Analog CCTV (DVR-based)
- BNC (coaxial) – Round connector with twist-lock, carries video signal.
- Power jack – 12V DC barrel jack from power adapter or power supply box.
- Sometimes combined as “video over coax + separate power”.
IP CCTV (NVR-based)
- RJ-45 Ethernet – For IP camera data + sometimes power (PoE).
- PoE Ports on NVR/switch – Provide power and data in one cable.
- HDMI / VGA – Output from NVR to monitor.
7️⃣ Power Ports
- IEC C13/C14 – Standard PC/server power cable (3-pin kettle cord).
- Figure-8 (C7) – Used on some laptops, consoles, small devices.
- Barrel jacks (DC power) – Routers, switches, CCTV cameras, small electronics.
- PoE (Power over Ethernet) – Power delivered through the RJ-45 cable to IP phones, APs, cameras.
8️⃣ Fiber & High-Speed Uplink Ports
- SFP/SFP+ – Small cages on switches/routers where you insert a fiber or copper module.
- LC, SC, ST connectors – Different shapes of fiber plugs; LC is most common in modern gear.
- QSFP – Larger modules for 40/100G in data centers.
Fiber ports are used for long distance links, building-to-building connections, or high-speed core networks.
9️⃣ Serial & Parallel / Legacy Ports
- DB-9 Serial – 9-pin connector still used for console access, industrial equipment, UPS management.
- DB-25 Parallel – Old printers & legacy devices.
- SCSI – Older servers/storage; wide multi-pin connectors.
You may not see these on modern office PCs but they appear in labs, factories, and old infrastructure you still have to support.
🔟 Card Readers & Misc Ports
- SD / microSD slots – Cameras, laptops, DVR/NVR backup.
- SIM card slots – 4G/5G routers and some laptops.
- Lightning – Apple devices (slowly replaced by USB-C).
✅ How to Identify Ports Quickly (Practical Checklist)
- Look for icons printed next to the port (network, headphone, mic, USB, HDMI symbol).
- Check color coding – green (audio out), pink (mic), blue (line-in), blue USB = 3.x, yellow LAN = WAN sometimes.
- Use the device manual or manufacturer diagram when in doubt.
- For CCTV, note whether it’s a DVR (coax/BNC) or NVR (RJ-45/IP) system.
- Label cables and ports in racks; future-you will be very thankful. 😄

Leave a Comment